React.js with its component-based architecture, allows developers to build modern, sleek interfaces. But, if that time saved is taken down by rigid templates, causing troubles connecting those powerful, modern front-end to a clunky, traditional CMS?
You're not alone.
What you need is to fetch content from a clean API, and have the freedom to render it however you see fit. Right? And to achieve that, you need a content management solution that doesn’t limit your content team and also doesn’t compromise your workflow or force you back into the codebase.
That is possible via modern CMSs, essentially, a headless CMS. The headless approach separates the frontend and backend, powering a flexible content modeling experience, robust API (like GraphQL or REST), and seamless integration with the React ecosystem, allowing developers to build fast, scalable, and decoupled React applications.
What is React JS?
As a developer building modern web applications, you know that React.js is a powerful JavaScript library for building dynamic and interactive user interfaces. You live and breathe its declarative nature and the efficiency it brings to your projects.
But for the sake of this discussion, let's zero in on the philosophy that makes React so transformative: its component-based architecture.
You don't think in terms of static pages; you think in systems of reusable, self-contained components. You build a <Navbar>, <UserProfileCard>, or a <ProductGrid>, each with its own logic, state, and markup.
This approach is what allows you to create complex, scalable, and maintainable applications with speed and precision. Your entire workflow is built around creating these building blocks and composing them into sophisticated UIs.
This is precisely where the friction with traditional content management systems begins. Those systems were built for a page-centric world. They often expect to control the entire HTML output, forcing your carefully crafted React components to fit into rigid, pre-defined templates.
You, the React developer, simply want clean, structured data that you can fetch and map to your components. You don't want a blob of pre-formatted HTML that fights with your code.
This fundamental need for pure data, not dictated presentation, is exactly why the concept of a headless CMS is the natural next step for any serious development with React.
What is a Headless Content Management System (CMS)?
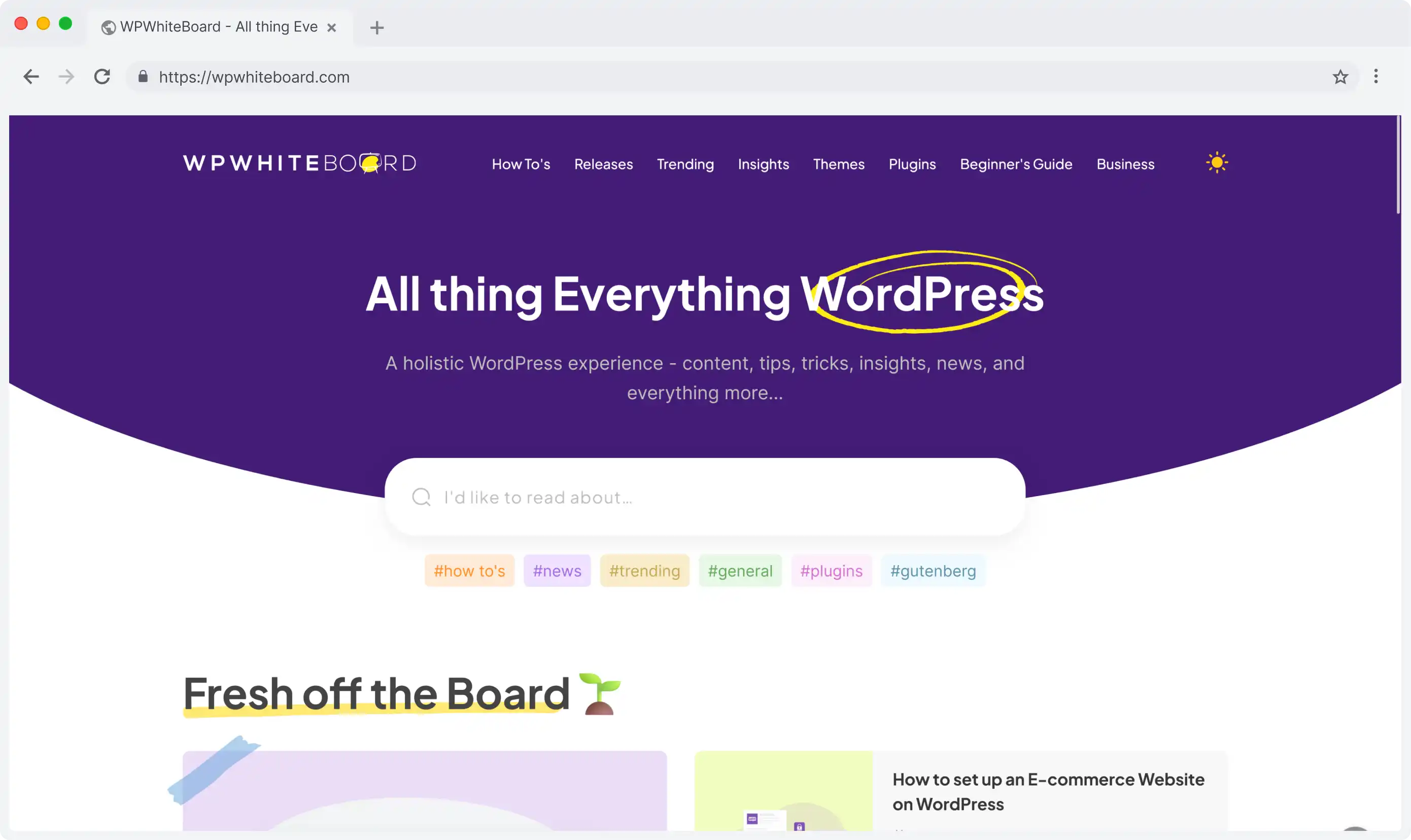
To understand what a headless CMS is, it helps to first think about a traditional, or monolithic, CMS. Systems like WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal were revolutionary in their time. They bundled everything into a single package: the back-end where you manage content (the "body") and the front-end templating system that renders the website (the "head").
This all-in-one approach is straightforward, but it’s also incredibly restrictive for a modern developer. The content is permanently bolted to the presentation layer.
A headless CMS takes a fundamentally different approach. It decouples the back-end content repository from any specific front-end presentation layer. It chops off the "head".
What you're left with is a powerful, focused system for creating, storing, and managing content, which is then made available to any front-end through an API.
Let’s make this concept instantly clear with a Lego analogy.
- A Traditional CMS is like a pre-packaged Lego set—say, the Millennium Falcon kit. You get all the specific pieces and a detailed instruction manual. It’s fantastic for building that one specific thing, but it’s nearly impossible to use those same pieces to build a castle. The content (the bricks) and the presentation (the instructions) are tightly coupled.
- A Headless CMS, on the other hand, is like a giant, unsorted bucket of universal Lego bricks. You have an endless supply of blocks in all shapes and sizes (your content). Your React application is your skill and imagination—you can use those same bricks to build the Millennium Falcon, a castle, a car, or even a mobile app.
In technical terms, the headless CMS is that bucket of bricks. It’s a back-end-only system focused purely on content management. It gives your content team a clean interface to create and structure content models and then provides you, the developer, with a powerful API (typically REST or GraphQL) to pull that content into any application you can imagine.
The result is that you get pure, structured JSON data—not opinionated HTML. You have total freedom to fetch that data and render it within your React components, on your terms. This is the perfect CMS for React.js because it doesn't fight your architecture; it fuels it.
Why a Headless Architecture is a Game-Changer for React Applications
Adopting a headless CMS is about fundamentally upgrading your entire development paradigm. For a developer who lives in the world of React, this shift from a coupled to a decoupled architecture solves the core frustrations you face daily. It bridges the gap between your desire to build beautiful, component-driven UIs and the practical need for a robust content management backend.
Here’s how a headless CMS for React.js directly improves performance, your workflow, and the long-term health of your applications.
With a traditional CMS, every page request often involves the server querying a database, loading a theme engine, processing plugins, and assembling an HTML page from scratch. This can be slow and difficult to scale.
A headless architecture obliterates this bottleneck. Your React application is a completely separate entity. You can build it as a static site (using frameworks like Next.js or Gatsby) or a client-side app that is served globally from a CDN. When it needs content, it makes a lightweight API call to the headless CMS. This results in:
- Blazing-Fast Load Times: Serving pre-built static files from a CDN is orders of magnitude faster than server-side rendering on a monolithic platform. This has a direct, positive impact on user experience and Core Web Vitals.
- Independent Scaling: Your front-end and back-end scale independently. A massive traffic spike to your React application won't overwhelm your content management system. You can handle millions of page views with confidence, knowing the CMS is only serving data when needed, not rendering every single page.
Giving Developers a Modern Workflow
This is where the magic truly happens for you as a developer. A headless approach gives you the freedom you’ve been looking for, creating a truly developer-friendly React CMS experience.
- Total Frontend Freedom: You are no longer trapped by restrictive templates. You have complete control over the markup, styling, and behavior of your application. You build your React components exactly how you want, using the tools you love, and simply pull in the data you need. This respects and amplifies the power of React’s component-based architecture.
- Parallel Development: The front-end and back-end teams can work concurrently. Your content team can define content types and populate entries in the CMS while you are building out the UI. This eliminates dependencies and dramatically speeds up your project timelines.
- Best-of-Breed Tooling: You get to use the best tool for every job. React for the UI, a headless CMS for content, a dedicated e-commerce platform for sales, and a specialized search service. This composable approach allows you to build more powerful and efficient applications than any single all-in-one system could provide.
Future-Proof Your Tech Stack
Choosing a headless architecture is a strategic decision that pays dividends for years to come. By separating your content from its presentation, you make your entire tech stack more resilient and adaptable.
- Omnichannel Content Delivery: The content in your CMS is now a central, reusable resource. You can deliver it to your React website, a native mobile app built with React Native, an email campaign, a digital kiosk, or any other platform you can dream up. You manage the content once and deliver it everywhere.
- Simplified Redesigns and Migrations: Need to redesign your website in two years? No problem. You can build an entirely new React application from the ground up, connecting to the exact same CMS API endpoint. The content remains untouched and secure. This makes future updates faster, cheaper, and far less risky, ensuring your React applications can evolve with technology.
Advantages of a Headless CMS with React.js
Pairing a headless CMS with React.js isn't just a technical choice; it's a strategic move that delivers clear, tangible benefits across your entire project lifecycle. By embracing this decoupled architecture, you unlock a superior way to build and manage modern web applications.
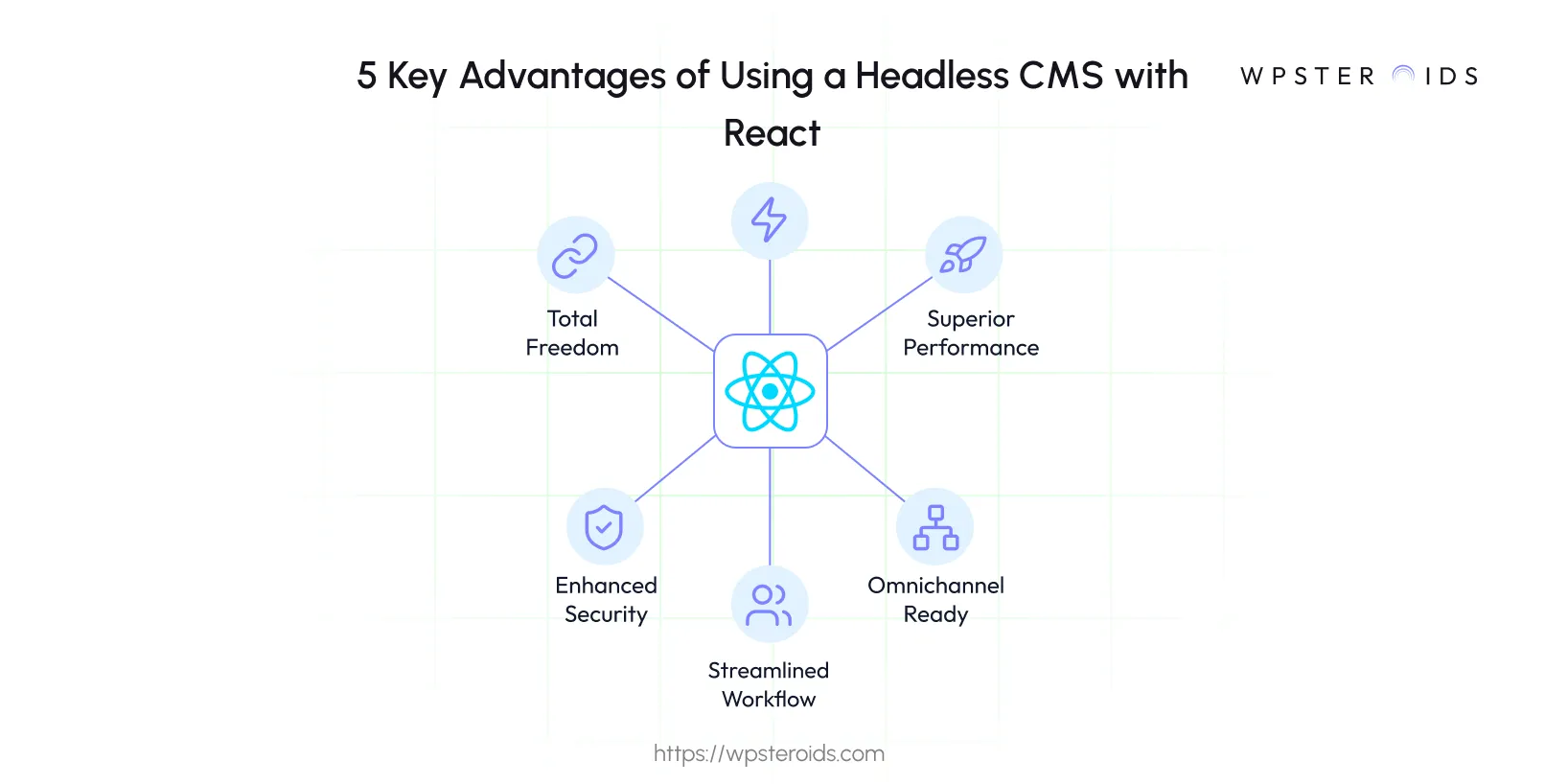
Here are the key advantages you can expect:
- Complete Creative and Technical Freedom: You are no longer constrained by the pre-defined themes or templates of a traditional CMS. With a headless approach, you have 100% control over the front-end. You can build your React components, structure your markup, and implement your design vision without any restrictions. The CMS delivers pure content via an API, and you decide exactly how it looks and functions.
- Superior Performance and Faster Load Times: Because your React front-end is decoupled, it can be built as a highly optimized static site or single-page application and deployed directly to a global Content Delivery Network (CDN). This means your users get blazing-fast load times, significantly improving user experience and SEO performance, as the heavy lifting of rendering pages is done at build time or on the client-side, not on a server for every request.
- Enhanced Security: A headless architecture reduces your application's attack surface. In a traditional setup, the CMS and the public-facing website are part of the same system. With a headless CMS, your content management back-end is entirely separate from the front-end. It isn't directly exposed to the public internet in the same way, making it much harder for bad actors to exploit potential vulnerabilities.
- Future-Proof, Omnichannel Content Delivery: Your content is no longer trapped in a single website. A headless CMS centralizes your content and serves it to any platform you need. You can use the same content repository to power your React website, a mobile app built with React Native, an IoT device, or even a digital display. This "create once, publish everywhere" model makes your content strategy incredibly efficient and ready for future channels.
- Streamlined Developer Experience and Team Workflow: A headless CMS creates a clear separation of concerns that allows your teams to work more efficiently. Your content editors can work within the user-friendly interface of the CMS—creating and managing content—while you and your development team focus solely on building the best possible front-end application using React. This parallel workflow shortens development cycles and eliminates bottlenecks.
Choosing the Right Headless CMS for React
The market for headless CMS platforms is crowded, and from the outside, they can all start to look the same. They all promise APIs, flexibility, and a better content management experience. But as a developer, you know the devil is in the details. The right choice can supercharge your workflow, while the wrong one can lead to months of frustration and technical debt.
So, how do you cut through the marketing noise and choose the best headless CMS for your React.js project?
It’s not about finding the longest feature list. It’s about evaluating platforms based on the criteria that directly impact your development process and the long-term health of your application. Here is a developer-centric framework to guide your decision.
A Crucial Factor: The Content Modeling Experience
While many guides focus on comparing feature lists, a far more strategic perspective for React developers is to evaluate each CMS on its Content Modeling Experience. The crucial question isn't just "Does it have a GraphQL API?" but rather, "How easily can my non-technical content team create structured, reusable content that I can map cleanly to my React components?"
Content modeling is the process of defining the structure of your content—creating fields, defining relationships, and setting validation rules. A superior content model means a cleaner, more predictable API response.
This translates directly into less data transformation code on your end and a more resilient application. It shifts the evaluation from a checklist of features to a more profound assessment of the developer-to-editor workflow.
Think about it: your goal is to fetch a JSON object that maps almost perfectly to the props of your <ArticlePage> or <ProductCard> component. A CMS with a flexible and intuitive content modeling experience, like with Contentful CMS, makes this possible.
One with a rigid or confusing system forces you to write complex logic to wrangle the data into the shape you need, defeating much of the purpose of using a modern CMS in the first place.
The API: Assessing GraphQL and REST Options
The API is the bridge between the CMS and your React application. Nearly all headless CMS platforms offer a REST API, which is a reliable and well-understood standard. However, for complex React applications, a GraphQL API is often a significant advantage.
- REST APIs are endpoint-based. You might have one endpoint for /authors and another for /posts. If you need to display a post along with its author's information, you often have to make multiple requests (one to get the post, another to get the author) or rely on the CMS to provide a "kitchen sink" endpoint with more data than you need.
- GraphQL APIs allow you to request exactly the data you need in a single call. You can specify the exact fields you want for a post and its related author in one query. This prevents over-fetching (getting useless data that slows down your app) and under-fetching (having to make multiple round trips to the server). For component-based architecture, this is a perfect match, as each component can define its own data requirements.
When evaluating a CMS, don't just check if it has GraphQL. Investigate the quality of its implementation. Is it well-documented? How does it handle relationships and filtering?
The Developer Experience: SDKs, Documentation, and Community Support
A great headless CMS is more than just its features; it's a tool that should make your life easier. The overall developer experience (DX) is a critical, and often overlooked, evaluation point.
- SDKs: Does the CMS provide a well-maintained JavaScript or React SDK? A good SDK can abstract away the complexities of API calls, caching, and authentication, saving you significant development time.
- Documentation: Is the API documentation clear, complete, and full of practical examples? Can you find answers to common questions quickly? The quality of the docs is often a direct reflection of how much a company cares about its developer community.
- Community Support: Is there an active community on platforms like Discord, Slack, or GitHub? When you run into a tricky problem, having a community of fellow developers to turn to can be an invaluable resource.
The "Developer Experience (DX) Tax"
I need to introduce a more critical concept: the Developer Experience Tax. This is the hidden cost you pay in developer time and energy to set up, integrate, and maintain your technology stack.
While competitors focus on which CMS is best, the more critical question for a developer is about "Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in terms of Developer Experience (DX)."
A headless architecture shifts costs. You save on server maintenance and licensing, but you increase complexity and the developer hours required for initial setup, integration, and maintaining the "glue code" between multiple services (content, search, forms, etc.).
A great headless CMS isn't just one with a good API; it's one that minimizes this "DX Tax" with excellent SDKs, robust documentation, and a supportive developer community.
Choosing a headless CMS with a low "DX Tax" is the single most important decision you can make. It means choosing a tool that accelerates your work, rather than one that creates new hurdles.
Every factor you consider should be viewed through this lens: "Will this feature reduce my DX Tax or increase it?"
Tackling the Challenges
- Technical expertise required
- User-unfriendliness
- Learning curve
- Higher costs
This confirms that the difficulty of making different services work together is a real and widespread problem. Therefore, when choosing a headless CMS for React.js, you should actively look for a platform that works to solve this challenge, not add to it.
Evaluate how easily the CMS integrates with the tools you use every day. Look for:
- Clear guides and starter kits for frameworks like Next.js.
- Seamless integration with deployment platforms like Vercel and Netlify.
- Robust webhook systems for triggering builds and other actions.
Choosing a headless CMS that prioritizes a smooth integration experience will save you countless hours of configuration and debugging, allowing you to focus on what you do best: building great applications.
The Top Headless CMS Options for React Projects in 2025
Now that you have a solid framework for evaluation, let's explore some of the best headless CMS platforms that excel in the React ecosystem. Each of these contenders offers a unique approach and philosophy.
The best CMS for you will depend on your specific project needs, your team's technical comfort level, and your priorities—whether that's ultimate control, a superior content modeling experience, enterprise-grade features, or a seamless visual editing workflow.
For Ultimate Customization and Self-Hosting: Strapi
Strapi is the leading open-source, self-hosted headless CMS. Built on Node.js, it gives you complete control over your content, your data, and your infrastructure. If you're a developer who loves to tinker, customize, and own your stack from top to bottom, Strapi is an exceptional choice.
- Why it's great for React: Since you host it yourself, you have the freedom to customize the API, create custom plugins, and integrate it with any database or service you need. The API responses are clean and predictable, making it easy to fetch data into your React components. Strapi provides both REST and GraphQL APIs out of the box.
- Best for: Teams who want full ownership of their data and codebase. It's ideal for projects that require deep customization of the admin panel or back-end logic. If the idea of vendor lock-in concerns you, the open-source and self-hosted nature of Strapi is a massive advantage.
For a Content-as-Code Approach: Sanity
Sanity stands out with its unique and powerful "content-as-code" philosophy. Instead of defining your content models through a graphical user interface (GUI), you define them as JavaScript objects in your codebase.
This developer-centric approach allows you to version control your content schemas with Git, reuse structures programmatically, and build incredibly sophisticated, custom-tailored editing experiences.
- Why it's great for React: Sanity's editing interface, Sanity Studio, is itself an open-source React application that you can completely customize. This allows you to build an editing environment that perfectly mirrors the structure and logic of your React components. It offers a powerful, real-time query language called GROQ in addition to a robust GraphQL API.
- Best for: Development teams that want the ultimate flexibility in their content structure and editing workflow. If your project involves complex, deeply nested data relationships, Sanity's programmatic approach to content modeling is second to none.
For Enterprise-Level Features: Contentful
Contentful is one of the pioneers in the headless CMS space and has matured into a robust, enterprise-ready platform. It is a fully managed, SaaS (Software as a Service) solution known for its scalability, reliability, and security.
For large organizations managing complex digital properties, Contentful provides the governance and workflow tools needed to operate at scale.
- Why it's great for React: Contentful's powerful content modeling UI and its well-documented APIs (both REST and GraphQL) make it straightforward to integrate with any React application. Its "App Framework" allows for seamless integration with other enterprise tools, and its performance and uptime are battle-tested, ensuring your application's content backend is always available.
- Best for: Large businesses and enterprises that need a proven, scalable, and secure platform with strong governance features like granular user roles, permissions, and complex content workflows. Teams that prioritize a reliable, managed service over deep customization will find Contentful to be a perfect fit.
For a Visual Editing Experience: Storyblok
Storyblok's key differentiator is its brilliant real-time visual editor. It masterfully bridges the gap between the flexibility of a headless architecture and the intuitive, in-context editing experience that content teams crave.
This is perhaps the best visual headless CMS for teams where editor adoption and ease of use are paramount.
- Why it's great for React: Storyblok’s entire philosophy is built around "bloks", which map directly to your React components. Your content team can visually build pages by selecting, arranging, and editing these blocks, seeing their changes reflected in real-time on the actual site layout. This creates an incredibly intuitive workflow for both developers and editors.
- Best for: Projects where a seamless and empowering editing experience is a top priority. It excels for marketing websites, landing pages, and any application where non-technical users need to create and manage complex page layouts without developer intervention.
Connecting a React App to a Headless CMS
Theory is great, but the real test is in the implementation. Seeing how cleanly a headless CMS integrates with a React app is the "aha!" moment for many developers. While the exact steps will vary slightly depending on the CMS you choose, the fundamental process is universal.
Let's walk through the high-level steps for bringing your content and components together.
Step 0: Prerequisites for Integration
Before you write a single line of code to connect the two systems, you'll need a few things in place. Consider this your pre-flight checklist:
- A React Development Environment: You should have a working local setup with Node.js and npm (or yarn) installed. A project scaffolded with a tool like Create React App or a framework like Next.js is a perfect starting point.
- Basic React Knowledge: You should be comfortable with core React concepts, particularly hooks like useState for managing component state and useEffect for handling side effects like API calls.
- A Headless CMS Account: You'll need to have signed up for one of the platforms mentioned earlier (or any other of your choice) and have access to its dashboard.
Step 1: Setting Up Your Headless CMS Project
Your first task is to give your content a home and a structure. This happens entirely within the headless CMS dashboard.
- Define Your Content Types: This is the most critical step. A "content type" (sometimes called a "model" or "schema") is the blueprint for your content.
For example, you might create a BlogPost content type. You would then define its fields: a title (plain text field), a slug (a URL-friendly text field), a featuredImage (a media/image field), and a body (a rich text field). This structured approach is what ensures you get clean, predictable data in your API responses. - Create Some Content: Once your content types are defined, create a few sample entries. Write one or two blog posts using the structure you just created. This gives you real data to pull into your React app for testing.
- Find Your API Credentials: Your CMS will provide you with an API endpoint (the URL you'll send requests to) and API keys or access tokens for authentication. Locate these and keep them handy.
Step 2: Integrating the CMS API with Your React App
Now it's time to shift gears and get into your React codebase. The goal here is to establish a secure and clean connection to the CMS API.
- Set Up an API Client: You'll need a way to make HTTP requests from your React app. You can use the browser's built-in fetch API, a popular library like axios, or—even better—a dedicated JavaScript SDK if your CMS provides one. The SDK often simplifies authentication and data fetching.
- Secure Your Credentials: Never hardcode your API keys directly in your components. This is a major security risk. The best practice is to store them in environment variables. Create a
.env.local file in the root of your project and add your credentials there, like this:
REACT_APP_CMS_API_URL=https://your-cms-endpoint.com/graphql REACT_APP_CMS_ACCESS_TOKEN=yourSecretTokenHere - Create a Service Layer: To keep your code organized, it's a great idea to create a dedicated service or module for all your CMS interactions. This abstracts the data-fetching logic away from your components. For example, you could create a file like services/cms.js to house all your API call functions. This step is key to properly integrating a react app with an external service.
Step 3: Fetching and Rendering Content Dynamically
This is where everything comes together. You'll now fetch the content from the CMS and render it using your custom React components.
- Fetch Data in a Component: Inside the React component where you want to display the content (e.g., BlogPage.js), use the useEffect hook to call your API service when the component mounts. You'll use the useState hook to store the data and manage a loading state.
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { getBlogPosts } from './services/cms'; // Your API service
const BlogPage = () => {
const [posts, setPosts] = useState(null);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
const fetchPosts = async () => {
const data = await getBlogPosts();
setPosts(data);
setIsLoading(false);
};
fetchPosts();
}, []); // Empty array means this runs once on mount
if (isLoading) {
return <p>Loading posts...</p>;
}
// ... rendering logic will go here
};
- Map Data to Your React Components: Once the posts state is populated, you can map over the array and render your data using the custom React components you've built. This is where the magic of decoupling shines—the structured data from the CMS flows seamlessly into the props of your React components.
// Inside the BlogPage component's return statement
return (
<div>
<h1>My Blog</h1>
{posts.map(post => (
<BlogPostCard
key={post.id}
title={post.title}
excerpt={post.excerpt}
slug={post.slug}
/>
))}
</div>
);
This simple, clean pattern is the core of how a headless CMS allows seamless integration react-ions with modern front-ends. You fetch structured data and render it with your components—no theme files, no weird template languages, just pure React.
The Full Lifecycle: Testing, Deployment, and Maintenance
Successfully connecting your React application to a headless CMS is a major milestone, but it’s just the beginning of the journey. As a professional developer, your responsibilities extend across the entire lifecycle of the project.
A robust strategy for testing, a streamlined deployment pipeline, and a clear plan for long-term maintenance are what separate a proof-of-concept from a production-grade application. Let's look at the best practices for managing your integrated React projects in the real world.
Strategies for Testing Your Integrated Application
Testing an application that relies on an external API requires a multi-layered approach. You need to ensure your components work as expected and that your integration with the CMS is solid, all without creating a fragile or slow testing suite.
- Unit Testing Your Components: Your individual React components should be tested in isolation. In this context, you are not testing the CMS API itself. Instead, you should mock the service layer that fetches the data.
Create a sample JSON object that mimics the API response and pass it as props to your component. This allows you to verify that your component renders the correct UI for a given data shape, handles loading and error states properly, and responds to user interactions as expected. - Integration Testing the Service Layer: This is where you test the actual connection. Write tests for your API service module (services/cms.js from our example) to confirm that it can successfully connect to the CMS endpoint, send a query, and correctly parse the response.
To avoid polluting your production data, the best practice is to connect to a dedicated "development" or "staging" environment within your CMS, which contains non-critical test data.
- End-to-End (E2E) Testing: Tools like Cypress or Playwright can automate a browser and simulate a complete user journey. You can write an E2E test that loads a live page, waits for the content to be fetched from the CMS, and asserts that a specific headline or piece of text is visible on the screen.
This is your final guarantee that the entire system—from the CMS through your application using react—is working in harmony.
Deployment Best Practices (Vercel, Netlify, etc.)
Modern hosting platforms like Vercel and Netlify are tailor-made for headless React applications, especially those built with frameworks like Next.js. They make deployment a seamless, automated process.
- Automate with Webhooks: The single most important concept to master is the webhook. When a content editor hits "publish" in the CMS, how does your live site update? You configure a "build hook" in your hosting platform (Vercel/Netlify) and paste that URL into your CMS's webhook settings.
Now, every time content is updated, the CMS sends a signal to that URL, telling your host to automatically re-build and deploy your site with the fresh content. This is the core of the modern Jamstack workflow. - Manage Environment Variables: As discussed earlier, your API keys and endpoints must be kept secure. Platforms like Vercel provide a simple UI for managing environment variables.
You can set different variables for your production, preview, and development builds, ensuring that your test branches connect to your staging CMS environment while your main branch connects to production. - Leverage Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR): For larger React applications, rebuilding the entire site for a single text change can be inefficient. This is where frameworks like Next.js truly shine. With ISR, you can configure pages to be re-generated on a timer or on demand when the data changes.
This gives you the incredible performance of a static site with the data freshness of a server-rendered one, providing an optimal experience for both users and content editors.
Long-Term Maintenance Considerations
Once your site is live, your job shifts to ensuring it remains healthy, secure, and adaptable for the future.
- Plan for Content Model Changes: Your application's requirements will evolve, and so will your content models. You might need to add a new field or change an existing one. Have a clear process for these "schema migrations."
This often involves updating the content model in the CMS, and then updating your React components to handle the new data structure, ensuring a smooth transition without breaking the live site. - Monitor API Performance and Usage: Keep an eye on the performance of your CMS. Are API responses getting slow? Are you hitting rate limits?
Most enterprise-grade CMS platforms provide dashboards for monitoring API usage and performance, which can help you diagnose and fix bottlenecks in your data-fetching logic. - Stay Updated: Your CMS and the libraries you use (including React itself) will have updates. Schedule regular time to apply security patches and updates to keep your application secure and benefit from the latest features.
A well-chosen CMS will have a clear policy on API versioning to prevent breaking changes from catching you by surprise.
Build Future-Proof Apps with React and Headless CMS
The journey from a monolithic, restrictive system to a flexible, decoupled architecture is one of the most empowering shifts a development team can make.
Pairing React with the right headless CMS is about more than just a new tech stack; it's about fundamentally improving how you build, manage, and scale digital experiences.
The power of this approach lies in its core principles. By decoupling your content from its presentation, you give your React developers the absolute freedom to build the best possible user interface, free from the constraints of rigid templates.
This separation is the key to unlocking superior performance, enhanced security, and the agility to deliver content to any channel—a website, a mobile app, and whatever comes next.
But the most critical takeaway is to change how you evaluate these tools. Moving beyond a simple feature checklist to focus on developer-centric criteria like the content modeling experience and the overall developer experience will lead you to a far better decision.
The best CMS for React isn't the one with the most features; it's the one that creates the most seamless and productive workflow between your developers and your content teams.
Ultimately, choosing the right headless react cms is about empowerment. It’s about giving your developers the tools they love, your content creators the intuitive environment they need, and your business the future-proof foundation it deserves.
Ready to see how a visual headless cms can transform your React development workflow and bring your teams together? Book your discovery call today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to set up a headless CMS?
Setting up a headless CMS involves a few core steps:
- Choose a Platform: Select a CMS provider (like Strapi, Sanity, Contentful, or Storyblok) and create an account.
- Define Content Models: Design the structure of your content. For example, create a "Blog Post" model with fields for a title, author, body text, and featured image.
- Create Content: Use the CMS interface to populate your content models with actual entries.
- Get API Credentials: Locate your API endpoint URL and the necessary access keys or tokens to authenticate your requests.
- Connect Your App: Use these credentials in your React application to start fetching content.
Is a headless CMS just an API?
No, it's more than just an API. A headless CMS is a complete back-end system for content management that uses an API for delivery. It includes a user-friendly interface for content creators, tools for defining content models, asset management for images and files, and user roles and permissions.
The API is a powerful delivery mechanism that makes your content available to any front-end.
Is a headless CMS a backend?
Yes, you can think of a headless CMS as a specialized "Content-as-a-Service" backend. It handles all the complexity of storing, managing, structuring, and delivering content, so you don't have to build that functionality from scratch. This allows you to focus solely on building a great front-end experience.
What are the benefits of using a headless CMS with React.js?
The primary benefits include:
- Total Frontend Freedom: Developers can build with React without being restricted by templates.
- Better Performance: Decoupled front-ends can be deployed to global CDNs, leading to faster load times.
- Enhanced Security: The content management back-end is separate from the public-facing application, reducing the attack surface.
- Omnichannel Delivery: You can use a single content source to power a website, mobile app, and any other digital platform.
Which headless CMS's are best suited for React.js?
The "best" CMS depends on your project's specific needs, but top contenders in the React ecosystem include:
- Strapi: Best for those who want open-source flexibility and self-hosting control.
- Sanity: Ideal for developer-centric teams who prefer a "content-as-code" approach with a customizable React-based editing studio.
- Contentful: A top choice for enterprise-level projects needing robust features, scalability, and security.
- Storyblok: Perfect for projects where an intuitive, real-time visual editing experience is a top priority for content teams.
How do I fetch content from a headless CMS in React.js?
You typically fetch content within a component using the useEffect and useState hooks. Inside useEffect, you make an API call to your CMS endpoint using the native fetch API, a library like axios, or the CMS provider's specific JavaScript SDK. The fetched data is then stored in state using useState, causing the component to re-render and display the content.
Can I use GraphQL with React and a headless CMS?
Yes, absolutely. Most modern headless CMS platforms offer a GraphQL API. This is a powerful combination for React applications because GraphQL allows your components to request the exact data they need in a single API call, which prevents over-fetching and leads to more efficient and performant applications.
What are the common challenges with integrating headless CMS in React.js projects?
The most cited challenge is integration complexity. This can involve setting up the initial build and deployment pipeline (including webhooks for content updates), managing environment variables securely, and ensuring a smooth workflow for handling changes to the content model over time.
Choosing a CMS with good documentation and starter kits for React can significantly reduce this complexity.
How scalable are React apps with a headless CMS?
This architecture is extremely scalable. Because the front-end (your React app) is decoupled from the back-end (the CMS), they can be scaled independently. Your React app can be served from a globally distributed CDN, capable of handling massive traffic spikes, while the CMS backend only needs to handle API requests, which is a much less intensive load.
Does using a headless CMS improve SEO with React applications?
Yes, it can provide a significant SEO boost. By using a headless CMS with a React framework like Next.js, you can pre-render your pages as static HTML (Static Site Generation). These static sites are incredibly fast, which directly improves your Core Web Vitals—a major Google ranking factor.
This architecture also makes it easy to ensure your server-rendered markup is clean, semantic, and easily crawlable by search engines.