Headless CMS scales and improves WPWhiteBoard’s content distribution, flexibility, and personalization
Sahil Mahalley
A Contentful content model defines the structure and organization of content within a space.
It is the total of all content types within that space, with each content type serving as a building block.
A contentful content model provides a blueprint that gives structure and organization to your content, telling APIs what kind of content to send to your end application.
A content model can be thought of as the "bones" of your project. It acts like a stencil or outline for your content, defining what data will be contained within each entry.
Just as an outline provides a framework for a document, a content model provides a framework for your digital content.
Purpose and Benefits of Content Modeling
Designing your contentful content model is critical in building a solid, efficient, and future-proof application.
It's not just a technical exercise, but a strategic process that involves understanding the needs of all stakeholders.
Content modeling in Contentful forms the backbone of how your content is structured and organized.
Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for building an effective content strategy.
Content types act as templates or building blocks within your content model. Each content type represents a distinct unit or module of content within your end application.
For example, a blog post, author profile, or product page would each be a separate content type, defining what data will be contained within individual entries.
Fields and Their Significance
Fields are the components that make up each content type, determining what data can be included in an entry.
They can range from simple text fields for titles and descriptions to more complex elements like media files or reference fields.
Each field can be configured with specific settings and validations to ensure content consistency and quality.
Fields can support up to 50 different specifications within a single content type.
Hierarchical Structure
Contentful follows a hierarchical approach to content modeling. At the top level are spaces, which contain multiple content types for your project.
Within this structure, content types can be linked to each other through reference fields, creating relationships between different pieces of content.
Space management is a fundamental aspect of contentful content modeling in Contentful.
Each space functions as a separate content database with its unique elements and permissions.
Best Practices for Space Usage Generally, consolidating content in one space is recommended, but certain situations warrant multiple spaces:
Appropriate Use of Multiple Spaces:
Avoiding Multiple Spaces For:
This structured approach to space management ensures efficient content organization while maintaining clarity and control over your contentful content model.
Before diving into content modeling, it's essential to shift away from traditional CMS thinking and embrace Contentful's flexible, modular approach to content structuring.
The key is to make the model fit your content needs, not the other way around.
When first logging into Contentful and creating a space, you'll be prompted to set up your content model.
This initial setup is crucial as it establishes the foundation for your content structure.
It's recommended to begin by considering your project's requirements and planning how content will be used across different channels.
To create content types, you can use several tools:
You can choose from various field types when adding fields to your content types depending on your needs.
Each field can be customized with:
The key is to consider how each field contributes to your overall content strategy and how it will be used in your end application.
Content modeling strategies in Contentful provide different approaches to organizing and structuring content based on specific business needs and use cases.
Each strategy serves unique purposes while maintaining content flexibility and reusability.
Different approaches to contentful content modeling help solve specific challenges, from content reusability to empowering editors and managing multilingual content.
Multichannel Modeling
This approach enables delivering personalized content across multiple channels, such as websites, mobile apps, and digital billboards.
It's particularly valuable for marketing and ecommerce teams, allowing quick market adjustments and targeted content delivery while maintaining separate editorial processes for different channels.
Navigation Modeling
This strategy defines the visual navigation structure for websites through side-menus, site maps, and breadcrumbs. It empowers editors to control site navigation without developer intervention, allowing immediate updates to site structure and navigation elements.
Topics and Assemblies
This pattern optimizes content for reuse by separating content into topics (what your site is about) and assemblies (content types that create structure).
While it requires a learning curve, it offers the greatest governance between editors and developers.
Localization
This approach handles content across multiple regions and languages.
It enables different versions of content for various locations, supports fallback languages, and allows separate editorial processes for different locales while maintaining content governance.
Microcopy Management
This strategy manages short, concise pieces of text like button labels and section headers. It empowers editors to handle UX design elements and SEO metadata without developer intervention.
These patterns define specific implementation approaches within your content model, focusing on structure and relationships between content types.
Fixed vs. Flexible Assemblies:
| Aspect | Fixed Assemblies | Flexible Assemblies |
| Definition | The reference field has only one referenced entry | Reference field can have many referenced entries |
| Example | SEO content type linked to webpage | Product carousel with multiple product entries |
| Usage | For content that should appear once | For collections of content |
| Control | Limited to one assembly | Empowers editors to organize collections |
| Best For | Metadata, single-instance content | Dynamic content, lists, galleries |
Content Hierarchy
Content hierarchy in Contentful uses a top-down referencing structure, similar to traditional page trees.
This allows defining relationships between content without limiting the model to specific contexts, making it ideal for representing website structure while maintaining content flexibility.
Avoiding Deep Nesting
While nesting (content referencing other content) is necessary, it's recommended to limit nesting to three levels or less.
Deeper nesting can confuse editors and make content management more complex. When editors work with deeply nested content, they can lose context of how properties apply to the website or application.
Understanding the distinction between content design and system design is crucial for effective content modeling.
Content Design System
A content design system consists of:
System Design Components
Basic system design provides structural guidance:
Content Context Requirements
Content design requires additional context considerations:
Context-Driven Decision Making
The key to effective content design is understanding:
Understanding content modeling becomes clearer through real-world examples.
These three practical models demonstrate how different content types can be structured to serve various purposes while maintaining flexibility and organization.
A blog post model starts with essential fields that capture all necessary information for each post.
The model includes:
This structure ensures consistent blog post formatting while maintaining flexibility for content creators.
The downloadable assets model consists of nine specialized fields designed to manage downloadable content effectively:
This model demonstrates how to structure content that requires both user interaction and file management capabilities.
This straightforward yet versatile model captures personal information efficiently through:
The Entity: Person model serves multiple purposes, from creating author profiles to building testimonial sections or team member pages.
Its simplicity makes it one of the most adaptable content models, easily integrated into various website sections like testimonial sliders, author pages, or blog post attributions.
Each of these models showcases different aspects of content modeling, from simple personal information management to complex downloadable asset structures, demonstrating how Contentful's flexibility can accommodate various content needs.
Contentful provides powerful tools and features that enable efficient Contentful content model creation, visualization, and management.
These tools help teams collaborate effectively while maintaining content structure integrity.
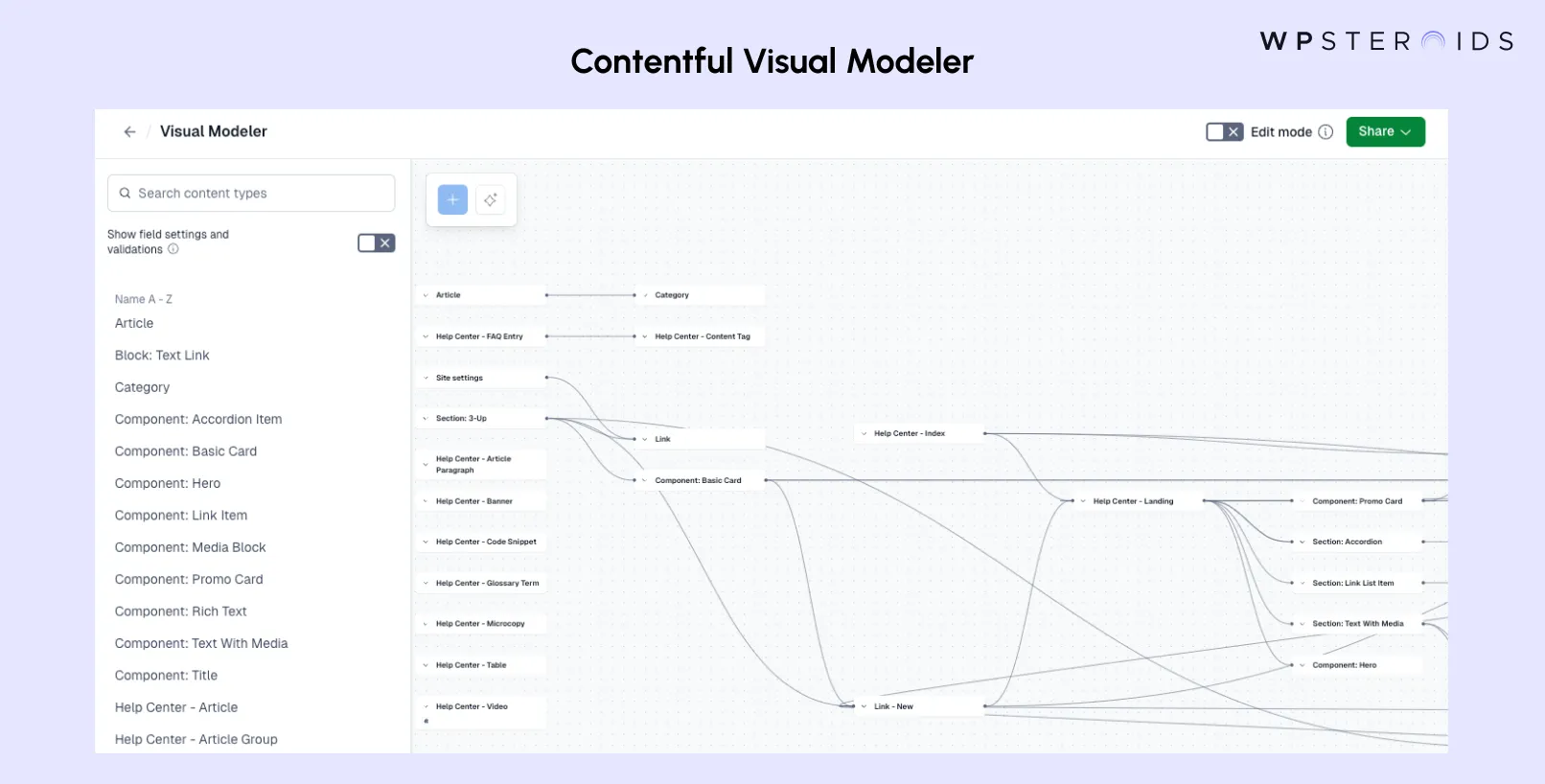
Edit vs. View Mode
The Visual Modeler operates in two distinct modes:
Actions and Capabilities
The Visual Modeler offers several key functions:
Field management encompasses the configuration and customization of individual fields within content types, ensuring content quality and user-friendly content creation.
Field Settings
Each field can be configured with specific settings, though field type and ID cannot be modified after creation.
Settings include:
Validations
The validations tab allows you to set specific requirements for each field:
Appearance Customization
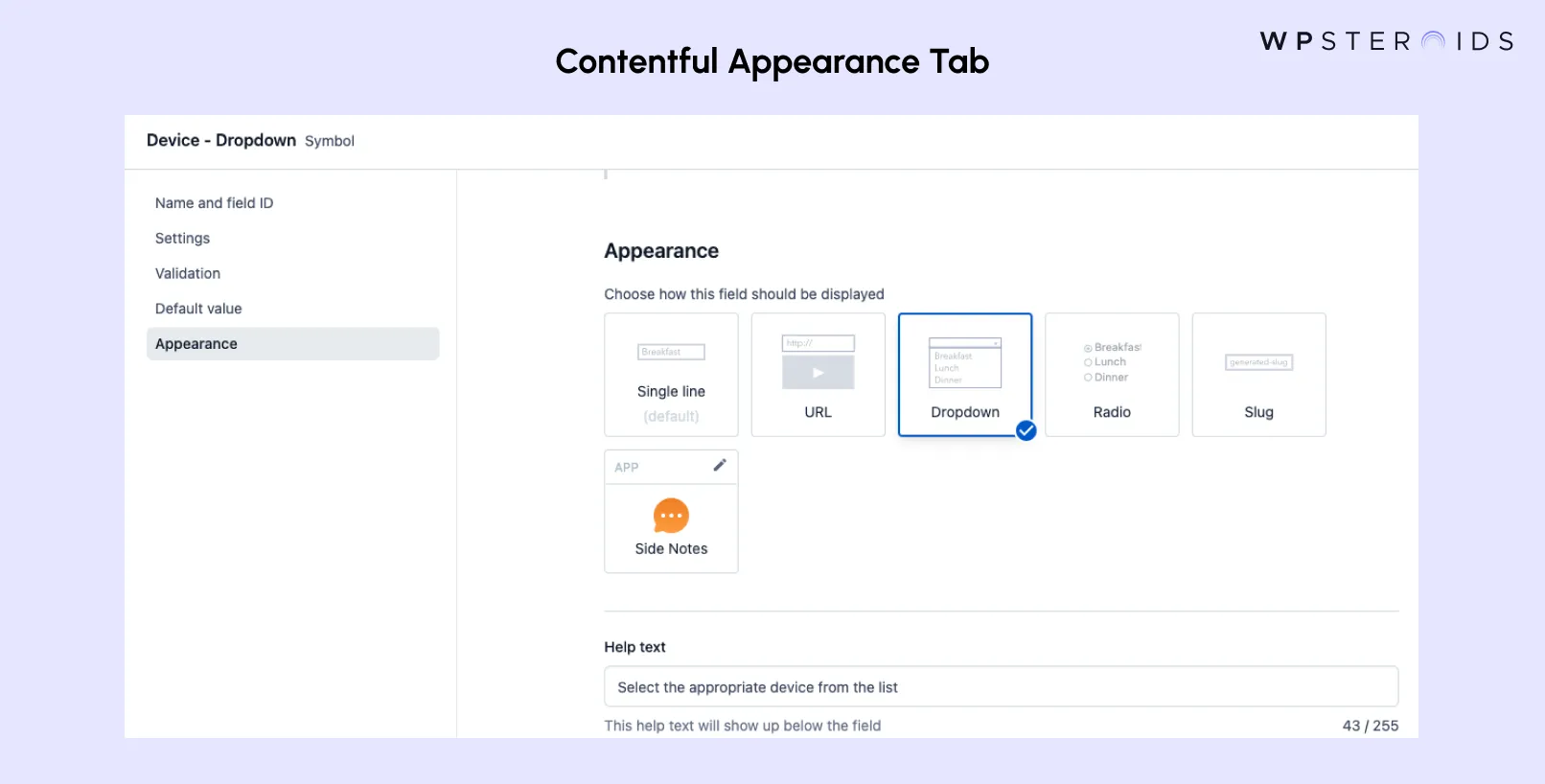
The appearance tab controls how fields display in the entry editor:
These tools and features work together to create a robust content modeling environment that supports both technical and non-technical team members in creating and managing content effectively.
Field visibility is a powerful feature in Contentful that allows you to control which fields are visible during content editing while maintaining their accessibility through the API.

Purpose and Benefits
Field hiding functionality offers several advantages:
Implementation Process
To hide fields while editing:
Permission Management
Proper field visibility control requires careful attention to permissions:
Best Practices
To optimize field visibility management:
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Watch for and address these common challenges:
Advanced Configuration
For more complex implementations:
This feature enhances content management efficiency while maintaining data integrity and accessibility through the API, making it a valuable tool for streamlining the content editing experience in Contentful.
Advanced techniques in Contentful enable more sophisticated content modeling approaches, allowing for complex relationships between content types and automated content management processes.
Reference fields create relationships between content types, enabling content reuse and structured relationships.
For example, a blog post can link to its author through a reference field, allowing the author's information to be reused across multiple posts.
Reference fields can be configured to:
Content modeling is an iterative process that requires collaboration between different team members to ensure effectiveness and usability.
The key to successful content modeling lies in constant refinement and testing.
Team Collaboration
Developers and editors play distinct but complementary roles in content modeling:
Iterative Development Process
Building a robust and scalable content model involves:
Content models are dynamic structures that evolve with your project needs. Contentful provides various tools and methods for managing these changes effectively.

Duplicating Content Types
When making significant changes:
Deleting Content Types
Follow these important steps when removing content types:
Contentful offers AI-powered content type generation to streamline the modeling process.
This feature:
Through the API, you can:
These advanced techniques provide greater flexibility and efficiency in content modeling, especially for larger projects or teams requiring automated processes and complex content relationships.
Note: While these techniques offer powerful capabilities, they should be implemented thoughtfully with consideration for your team's needs and technical capabilities.
Selecting Your Content Modeling Approach
A content model is more than just a structure - it's the foundation of your digital presence.
When choosing your approach to content modeling, consider:
Contentful provides various resources to help you succeed with content modeling:
Before implementing your contentful content model:
Remember that content modeling is an iterative process. Start with a solid foundation, but be prepared to adapt and evolve your model as your needs change.
The goal is to create a flexible, scalable structure that supports your current needs while accommodating future growth.
Contact us for implementations or specific guidance, to help you optimize your content model for your specific use case.
